Imagine deep sea exploration without a map. That’s what entering a business transaction without a due diligence audit is like. Just as a map reveals hidden currents and potential obstacles, a due diligence audit uncovers risks and opportunities that could make or break the journey ahead.
Join us as we explore the essential steps, strategic benefits, and modern solutions that make the procedure a catalyst for informed decision-making and sustainable growth.
🔲 Before we start!
This article examines a due diligence audit, which inherently involves the concept of due diligence itself. This inclusion is deliberate to ensure a comprehensive grasp of the topic for all readers, whether new to the subject or seeking a deeper understanding.
What is a due diligence audit?
A due diligence audit is a thorough internal investigation conducted to verify a company’s readiness for sale. Typically, companies perform it before a merger, acquisition, investment, or other significant transactions. The purpose of a due diligence audit is to assess the risks and opportunities associated with the deal.
In particular, the procedure reveals whether the company has highly fluctuating revenue, indicating potential instability. On the other hand, a due diligence audit may uncover untapped revenue streams or market segments that the business could exploit for growth. Either way, this procedure is crucial for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
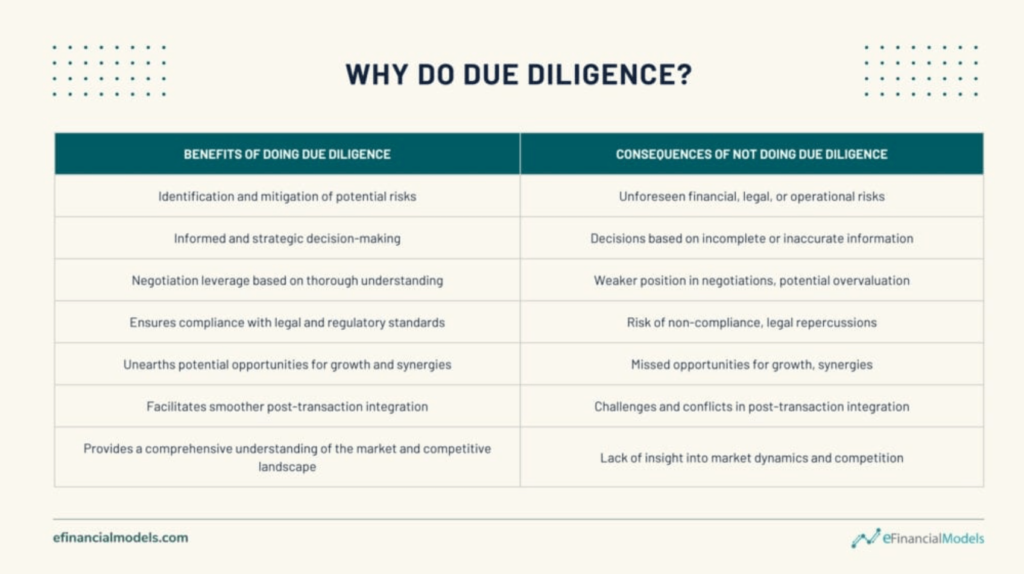
Who conducts a due diligence audit?
Typically, these are accountants, lawyers, consultants, or specialized firms with expertise in financial analysis, legal matters, and risk assessment. Still, the specific team involved may vary depending on the nature of the audit.
Next, we briefly outline the main types of due diligence audits. This will help with understanding the comprehensive nature of this investigation and its role in evaluating various aspects of a target company.
What are the types of due diligence audits?
Depending on its purpose, due diligence involves examining different aspects and, therefore, takes the following forms:
| Type | Value |
| Financial due diligence |
🔸 Evaluating the target’s financial health and performance 🔸 Reviewing financial statements, cash flows, assets, liabilities, and revenue streams 🔸 Verifying the accuracy of financial information and assessing risks and opportunities |
|
✏️ Checkout a financial due diligence example, checklist, and red flags |
|
| Legal due diligence |
🔸 Examining the legal aspects of the company, including contracts, agreements, and legal obligations 🔸 Assessing litigation history, intellectual property rights, regulatory compliance, and potential risks 🔸 Identifying legal issues or liabilities that could affect the transaction |
| Operational due diligence |
🔸 Evaluating the operational aspects, such as business processes, supply chain, and infrastructure 🔸 Assessing operational efficiency, scalability, and potential risks, such as dependencies on key suppliers or customers 🔸 Identifying opportunities for operational improvement and assessing readiness for future demands |
|
✏️ Checkout the operational due diligence example’s checklist to gather all essential data |
|
| HR due diligence |
🔸 Reviewing employee contracts, personnel files, and payroll records 🔸 Evaluating the organization’s hierarchy, reporting lines, and responsibilities 🔸 Identifying key personnel, critical roles, and talent management practices to assess the company’s ability to retain and develop its workforce |
| Tax due diligence |
🔸 Examining the company’s tax returns, filings, and records to verify compliance 🔸 Identifying potential tax risks or liabilities that could arise from past performance 🔸 Ensuring that the target complies with all applicable laws and regulations |
Other types of due diligence include commercial, environmental, technical, and cultural. Each probe focuses on specific aspects of businesses, providing valuable insights to stakeholders and helping them make informed decisions.
| ✏️ Additional resources: What is commercial due diligence? |
Our next step is to discover how to conduct the procedure with maximum benefit. The following is the most effective roadmap developed by our expert.
How to do a due diligence audit?
Just follow the steps and tips below.
1. Establish objectives
Clearly define the purpose and scope of the due diligence audit. For example, you may aim to assess the company’s financial stability, identify legal risks, or assess technology assets.
Best practices:
- Communicate the objectives to all team members clearly
- Prioritize goals based on their significance and potential impact on business outcomes
- Regularly revisit and refine objectives as new information is gathered
2. Gather information
Collect and examine the company’s relevant documents, including financial records, legal documents, operational reports, and HR data.
Best practices:
- Develop a comprehensive due diligence audit checklist and ensure nothing is overlooked
- Use online solutions such as data rooms to organize and centralize information
- Assign specific team members responsible for gathering different types of documents
3. Conduct financial due diligence
Review the company’s financial statements, including income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and tax returns. Analyze key metrics such as revenue growth, profitability, liquidity, and solvency to assess the company’s financial performance.
Best practices:
- Engage experienced financial professionals to conduct a thorough analysis
- Utilize financial modeling and forecasting techniques to project future performance and assess company-specific risks
- Cross-reference financial information with other due diligence findings to validate data accuracy
4. Conduct legal due diligence
Conduct a thorough documentation review of legal documents and contracts to identify potential issues. Assess the terms, obligations, rights, and liabilities under each contract. Also, pay attention to potential breaches or disputes.
Best practices:
- Involve legal experts or specialized attorneys to conduct a detailed legal scrutiny with professional support
- Create a structured framework or checklist to analyze each contract systematically
- Pay close attention to legal issues or discrepancies that may have significant implications for the transaction or the ongoing operations
5. Conduct operational due diligence
Evaluate the company’s business practices, processes, and systems to gauge efficiency and scalability and identify improvement opportunities. It may involve site visits, interviews with company representatives, and analysis of operational data and performance metrics.
Best practices:
- Create detailed process maps of the target company’s key operations to visualize workflows and identify bottlenecks
- Use anonymous employee surveys to gather insights on challenges and workplace culture
- Compare the target’s operational performance metrics against industry benchmarks to identify areas where this business excels (or lags)
Check this out!
We highlighted various types of audits in this section. However, each depends on the deal’s nature and specific transactional requirements.
For instance, a detailed technology due diligence audit may be optional in an asset purchase agreement because a buyer is primarily interested in acquiring tangible assets. However, in a merger or acquisition involving a technology company, a technology due diligence audit would be critical to assess the quality and security of the target’s tech infrastructure.
6. Assess risks
Identify and evaluate potential risks and liabilities associated with the transaction. Evaluate their possible impact on the business and develop strategies to mitigate or manage them.
Best practices:
- Perform scenario planning to assess how different risks might impact the business under various conditions
- Involve cross-functional teams in the assessment process to ensure a comprehensive evaluation from different perspectives
- Analyze historical data and past incidents related to the company to identify patterns and recurring risks
7. Report audit findings
Compile a comprehensive audit report summarizing everything revealed during your due diligence audit. Provide recommendations and insights to help stakeholders make informed decisions about the transaction.
Best practices:
- Present findings in a clear and concise manner in the due diligence report
- Utilize charts, graphs, and visual aids to make the information easier to perceive
- Provide contact information for the due diligence audit team or key personnel who can answer specific queries or provide further details
| ✏️ Learn more: How to write a due diligence report? |
What are the key benefits of due diligence audits for both parties?
For your convenience, we have categorized the advantages into those for sellers, buyers, and both.
For a buyer
- Informed decision-making. A due diligence audit thoroughly explains the target company’s financial health, operations, and market position. As a result, the buyer can accurately assess the deal’s value
- Risk identification. Recognized risks enable the buyer to make informed decisions about whether to proceed with the transaction and on what terms
- Integration planning. Understanding the company’s operations, culture, and systems helps the buyer plan for post-acquisition integration and ensure a smoother transition
For a seller
- Building shareholder trust. Transparent due diligence materials can earn buyers’ trust and demonstrate the seller’s commitment to openness
- Highlighted strengths. A well-prepared due diligence package demonstrates the company’s competitive advantages in the best light and makes it more attractive to buyers
- Minimized delays. Anticipating and addressing potential concerns during a due diligence audit minimizes transaction slowdowns and disruptions
For both parties
- Expectations alignment. A clear understanding of the business reduces the risk of post-transaction disputes
- Smooth preparation for integration. Both parties can plan better for the integration phase and ensure quicker realization of synergies
- Foundation for future collaboration. Transparency in transactions, which a due diligence audit gives, lays the groundwork for a positive and long-term relationship between the buyer and the seller
After understanding the concept of a due diligence audit, including its types, steps, and benefits, we can discuss the challenges that businesses may encounter throughout the procedure.
What are common challenges in a due diligence audit?
Companies face various complications during audits, depending on their size, industry, and level of readiness. For example, due diligence in healthcare acquisitions often encounters significant challenges related to regulatory compliance. Therefore, it’s important to be mindful of potential obstacles and know how to address them.
- Incomplete or inaccurate information. Obtaining all necessary documents proves challenging due to discrepancies or missing details
- Limited time to conduct thorough due diligence. Pressure to close the deal quickly restricts the depth of the investigation
- Managing and analyzing large volumes of complex data. Handling extensive and intricate information requires careful organization and analysis
- Miscommunication between parties. Language barriers or differing business practices can hinder effective communication
- Limited access to key management and employees. Restricted availability of essential personnel impedes obtaining crucial insights throughout the due diligence process
- Navigating different regulatory environments. Understanding and complying with diverse regulatory frameworks presents complexities
- Assessing the compatibility of company cultures. Evaluating the alignment of organizational cultures requires careful observation and analysis
Finally, we have arrived at the point where we can explore the solutions to overcome these challenges.
The role of technology in due diligence audits
There are various online solutions, each serving different purposes, from data and project management to collaboration tools. However, a virtual data room, one of the most popular platforms among business leaders, can meet all needs in one easy-to-use space.
| ✏️ Learn more: Essential M&A Tools and Software for Dealmakers in 2024 |
What is a virtual data room?
A virtual data room (VDR) is a secure platform for storing and sharing sensitive documents, collaborating, and managing workflows. One of the key software features is the high level of data security, which is crucial for managing confidential information during business transactions.
Most commonly, datarooms are used for mergers and acquisitions and due diligence. Other use cases include initial public offerings, strategic partnerships, fundraising, and real estate transactions.
What is data room functionality for a due diligence process?
We categorized software features to demonstrate how the platform streamlines the procedure in different aspects. Please note that the following list covers only some data room functionalities for a due diligence audit.
Data security
- Robust encryption. Use AES-256-bit encryption for data at rest and SSL/TLS protocols for data in transit to protect confidential information.
- Granular permissions. Apply role-based access control to define and restrict user access to specific due diligence documents and actions.
- Two-factor authentication. Enhance security by requiring a second form of verification.
- Dynamic watermarking. Apply customizable watermarks on documents to deter unauthorized sharing and copying.
- Access expiration. Set expiration dates for access to specific documents or entire projects.
- IP and time access restrictions. Limit access based on IP addresses or block of time to strengthen security.
- Fence view. Restrict users from viewing certain sections of documents to prevent unauthorized access.
- Audit logs. Track all user interactions and actions within the data room with detailed activity reporting.
Document management
- Bulk drag-and-drop upload. Easily upload large volumes of due diligence documents by dragging and dropping them into the designated area.
- Auto indexing. Automatically organize and tag documents as they are uploaded, making them easily searchable and accessible within the platform.
- Full-text search. Allow users to locate specific content quickly using keywords or search filters.
- Version control. Track document versions to ensure users access current information.
- Multiple format support. Ensure compatibility with various file formats, including PDFs, Microsoft Office files, images, and videos.
Collaboration
- Q&A section. Facilitate efficient and traceable communication between parties with dedicated spaces for exchanging due diligence audit questions and answers.
- Annotations and notes. Enhance collaboration and feedback throughout a due diligence audit by allowing users to add annotations and notes to documents.
- Email notifications. Keep all parties informed of document updates and activity with real-time email alerts.
- Task management. Streamline workflow and project management by assigning tasks and setting deadlines within the platform.
- User groups. Facilitate easier collaboration and permissions management by organizing all due diligence parties into groups.
Compliance
- Regulatory compliance. Meet diverse regulatory requirements, such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOC 2, SOC 3. and ISO/IEC 27001:2013.
- Access reports. Create detailed reports on user access and document activity to uphold compliance and provide oversight.
- Secure document deletion. Safely and permanently delete data in accordance with compliance requirements.
Additional features that simplify the due diligence audit process include remote shred, built-in redaction, multi-project management, workspace customization, and mobile apps.
Explore the top five virtual data room solutions to gain more insights into this platform and choose the best one for your team.
Conclusion
- A thorough due diligence audit is an essential and strategic part of M&A transactions, benefiting buyers and sellers.
- The main steps include establishing objectives, gathering data, conducting financial, legal, and operational due diligence, assessing risks, and reporting findings.
- A comprehensive due diligence audit brings numerous advantages to a company, including mitigated risks and improved stakeholder confidence.
- Virtual data rooms play a crucial role in streamlining the due diligence process by addressing data security, document organization, and collaboration challenges.

