Nov 05 ‘25
27 min read
No time to read? Get a quick AI summary
In M&A, due diligence empowers sellers to control narratives, resolve risks early, and maximize valuations. This guide explores its strategic role, offering a checklist and actionable steps to organize documentation, leverage virtual data rooms, and anticipate buyer concerns. It turns preparation into a competitive edge for smoother, more profitable transactions.

What is sell-side due diligence?
Sell-side due diligence is a structured evaluation process initiated by a seller to prepare their business for a merger, acquisition, or sale. It involves a thorough review of the company’s financial, legal, operational, and commercial standing to present a transparent, compelling narrative to potential buyers.
Unlike reactive approaches, this proactive exercise positions sellers to address weaknesses, clarify ambiguities, and highlight strengths, ensuring they enter negotiations with confidence and control.
Sell-side vs. buy-side due diligence: Key differences
While both processes aim to validate a company’s value, their objectives and execution differ significantly. Buy-side due diligence is buyer-driven, focusing on uncovering risks, validating assumptions, and justifying the investment.
In contrast, sell-side due diligence is seller-led, designed to streamline the transaction by preemptively resolving issues that could derail a deal. Sellers curate the information flow, ensuring critical data, from financial records to customer contracts, is organized and defensible.
This proactive approach is becoming increasingly common, with the U.S. sell-side due diligence services market valued at $971 million in 2024 and projected to reach $2.16 billion by 2033, reflecting growing demand for structured, seller-prepared documentation.
The strategic purpose for sellers
From the seller’s perspective, this process serves three core objectives:
- Anticipating buyer concerns: By conducting an internal assessment, sellers identify red flags (e.g., customer concentration, pending litigation) and prepare rebuttals or solutions. For example, if a buyer questions declining margins, the seller can proactively explain cost-saving initiatives already in motion.
- Controlling the narrative: Sellers emphasize competitive advantages, such as proprietary technology or loyal client bases, while contextualizing less favorable metrics.
- Maximizing valuation: Transparent, well-documented operations reduce buyer uncertainty, often leading to higher offers and fewer renegotiations.
Why sell-side due diligence matters
Sell-side due diligence isn’t just a procedural hurdle—it’s a strategic tool that directly influences deal success. Here is a list of benefits of seller preparations:
Mitigating deal-killing risks
Every M&A transaction carries inherent risks, and executives prioritize key vulnerabilities: 96% of respondents in the AON survey expect ESG scrutiny in deals to surge over the next three years, while 86% would abandon a transaction over material cybersecurity risks.
“A raft of new legislation means businesses must comply with a whole range of emerging due diligence and transparency requirements.” PwC
The proactive sell-side due diligence process can uncover compliance issues and red flags early, giving sellers time to remediate problems or craft compelling explanations.
Building buyer trust
Buyers often enter deals with skepticism. However, a seller with a meticulously prepared data room, organized financials, validated forecasts, and clean contractual records signals professionalism and transparency.
This credibility accelerates buyer decision-making, as their teams spend less time verifying basic facts. In auctions, this trust can ignite competitive tension, driving valuations upward.
Accelerating transaction timelines
M&A delays erode value, and due diligence for sellers takes longer than ever these days. Buyers now demand deeper scrutiny: lower-middle market closings once averaged 45 days post-LOI in 2021 but now stretch to 60–90 days.
Lengthy buyer-led investigations often trigger “discovery fatigue,” where late-emerging issues force renegotiations. Sell-side preparation flips this dynamic by addressing buyer questions upfront through a well-timed disclosure schedule, compressing timelines.
For example, preemptively explaining a customer churn spike with a rebound strategy keeps buyers focused on future potential, not past performance, while offsetting today’s extended diligence expectations.
Strengthening negotiation power
A well-prepared seller doesn’t just react—they dictate terms. By showcasing resolved risks and validated growth levers, sellers shift conversations from “why discount?” to “why wait?” This confidence permeates negotiations, whether defending valuation multiples or resisting overly restrictive warranties and representations.
Who should be involved in the process?
A well-coordinated team is critical to executing a transaction effectively. Each member brings expertise to address specific risks, streamline disclosures, and reinforce the seller’s strategic narrative. Here is a role chart for the sell-side M&A preparation.
| Due Diligence Team | Key Responsibilities |
| M&A advisors/investment banks/private equity firms | Lead valuation analysis, buyer outreach, deal structuring, and negotiation strategy. |
| Financial advisors | Audit financial statements, refine EBITDA adjustments, and prepare growth projections. |
| M&A lawyers | Review contracts, intellectual property, compliance, and draft disclosure schedules. |
| Management team | Provide operational insights, clarify buyer questions, and validate business strategy. |
| VDR providers | Manage secure document sharing, permissions, and real-time activity tracking. |
| External specialists | Address niche risks (e.g., environmental audits, IT security assessments). |
Preparing for sell-side due diligence
A successful M&A transaction hinges on meticulous preparation. For sellers, this means treating the process not as a reactive scramble but as a strategic opportunity to showcase value, mitigate risks, and align stakeholders. Below, we outline actionable steps to prepare effectively, along with the advantages of starting early.
Benefits of conducting assessments early
Initiating seller assessments months before engaging buyers offers transformative advantages. It allows sellers to identify and resolve issues that could devalue the business or stall negotiations.
For example, a software company might discover gaps in intellectual property ownership during an early audit, a fixable problem that, if unaddressed, could crater buyer confidence.
Moreover, early preparation fosters alignment among stakeholders. Founders, investors, and management often have divergent priorities, but a structured process can harmonize these perspectives, ensuring a unified front during buyer discussions.
Finally, early preparation reduces stress. By curating documents, refining financial models, and stress-testing assumptions ahead of time, sellers avoid the chaos of last-minute requests and maintain leverage in negotiations.
Step 1: Conduct an internal corporate audit
Begin with a candid assessment of your business’s financial, legal, and operational health. Engage external auditors or consultants to review financial statements, tax records, and compliance frameworks.
This audit should mirror what a buyer’s team will perform, targeting areas like revenue recognition practices, pending litigation, or regulatory adherence.
For instance, a manufacturing company might audit its supply chain contracts to ensure they’re transferable post-sale, avoiding surprises during buyer investigation.
Step 2: Organize critical seller documentation
Buyers expect instant access to clean, well-structured records. Start by compiling:
- Financial records: Audited financials, tax returns, accounts receivable/payable aging reports, and debt schedules.
- Legal documents: Articles of incorporation, shareholder agreements, employment contracts, and intellectual property filings.
- Operational data: Customer/supplier contracts, inventory reports, IT system diagrams, and facility leases.
- Strategic materials: Market analyses, growth projections, and competitor benchmarking.
Step 3: Craft a compelling narrative
Buyers often invest in stories rather than just acquire assets. Develop a cohesive narrative that explains past performance, justifies current valuation, and highlights future potential.
For example, if your SaaS company’s revenue dipped during a product transition, frame this as a strategic pivot with a roadmap showing renewed growth.
This narrative should permeate all materials, from the executive summary to financial forecasts, ensuring consistency when buyers probe for weaknesses.
Step 4: Stress-test your valuation
Work with financial advisors to validate your asking price. This involves refining EBITDA adjustments (e.g., add-backs for one-time expenses), benchmarking against recent industry transactions, and modeling downside scenarios.
If a buyer challenges your valuation, robust models and market comparisons provide defensible counterarguments. For instance, a retail business might highlight premium valuations for brands with similar customer loyalty metrics, even if EBITDA margins are temporarily compressed.
Step 5: Anticipate buyer questions
Buyers will scrutinize every aspect of your business. Preempt their concerns by:
- Addressing customer concentration: If 40% of revenue comes from one client, prepare a plan to diversify post-sale.
- Explaining historical volatility: Clarify anomalies in financials (e.g., a spike in R&D costs tied to a patent launch).
- Validating projections: Link forecasts to tangible drivers, like signed contracts or market expansion plans.
Role-play Q&A sessions with your team to refine responses and ensure alignment.
Step 6: Align stakeholders
Hold workshops with founders, investors, and key employees to align on goals, timelines, and post-sale roles. For example, a founder planning to retire post-acquisition should clarify their transition plan early to avoid buyer concerns about leadership continuity.
Step 7: Conduct a mock due diligence
Simulate the buyer’s process by inviting a third party (e.g., a consultant or law firm) to review your materials and examine the standard due diligence checklist. Their feedback can reveal overlooked gaps, such as missing environmental permits or unclear SaaS revenue recognition policies.
Sell-side due diligence checklist
A robust due diligence checklist for selling a business is the backbone of an effective merger or acquisition process. It ensures no critical detail is overlooked, streamlines buyer interactions, and positions your business as a well-prepared, low-risk opportunity.
Below, we’ve organized a comprehensive checklist by category, with actionable steps to anticipate buyer demands and simplify the process.
Key categories & diligence documents to prepare
Use this table to organize materials and address buyer priorities.
| Category | Documents & Actions | Notes |
| Financial | – Audited financial statements (3–5 years) – Tax returns and filings EBITDA adjustments with explanations – Debt/liability schedules – Accounts receivable/payable aging reports – Financial projections (3-year) | Highlight non-recurring expenses (e.g., litigation costs) and normalize EBITDA. Include footnotes for unusual trends. |
| Legal | – Articles of incorporation and bylaws – Shareholder/partnership agreements – Pending litigation history – IP registrations/licenses – Regulatory compliance certificates – Lease/real estate agreements | Flag expiring contracts or non-transferable licenses. Summarize litigation risks in a memo. |
| Operational | – Supplier/vendor contracts Inventory reports (current and historical) – IT system diagrams/data flow – Facility maintenance records – Production capacity/utilization data | Note any single-source suppliers or geopolitical risks. Include disaster recovery plans. |
| Commercial | – Customer contracts (key accounts) – Sales pipeline and backlog – Market analysis reports – Competitor benchmarking – Marketing strategy/ROI metrics | Disclose customer concentration (>10% revenue). Provide churn rates and retention strategies. |
| HR & Compliance | – Employee contracts and handbooks – Benefit/pension plan details – OSHA/EEOC compliance records – Organizational chart – Union agreements (if applicable) | Highlight key personnel retention plans. Address pending labor disputes proactively. |
| Strategic | – SWOT analysis – Growth roadmap (new markets/products) – Synergy opportunities for buyers – ESG initiatives and reporting | Align growth plans with industry trends (e.g., AI adoption). Quantify ESG-related cost savings. |
Pro tips for maximizing checklist effectiveness
- Assign ownership: Designate team leads for each category (e.g., CFO for financials, General Counsel for legal).
- Version control: Use a virtual data room to ensure all documents are updated, watermarked, and trackable.
- Contextualize data: Attach brief memos to complex items (e.g., “Why Q2 2023 Revenue Dropped 15%”).
- Redact sensitive data: Mask confidential info (e.g., customer names) until LOI is signed.
- Update continuously: Treat the checklist as a living document and refresh it as new data emerges.
Anticipating buyer questions
The checklist isn’t just about documents; it’s a tool to predict and prepare for buyer inquiries. For example:
- Financial due diligence: Buyers may question add-backs. Preempt this with a detailed reconciliation of EBITDA adjustments.
- Legal due diligence: If IP ownership is split with a third party, draft a side letter explaining usage rights.
- Operational assessment: For inventory write-downs, provide a plan to optimize stock levels post-sale.
🔎 Additional reading: Get an actionable commercial due diligence framework in our dedicated article.
Common pitfalls to avoid
- Overlooking “soft” assets: Document intangible value drivers like brand reputation or employee expertise.
- Ignoring regional compliance: If operating globally, include country-specific tax filings or labor laws.
- Underestimating IT diligence: Prepare cybersecurity audits and SaaS stack redundancy plans.
How virtual data rooms support sell-side due diligence
Virtual data rooms (VDRs) have become indispensable in modern mergers and acquisitions, transforming fragmented transaction readiness activities into streamlined, secure workflows.
By centralizing critical functions like document sharing, version control, and buyer access, a VDR for due diligence mitigates risks inherent in traditional methods while accelerating transaction timelines. Below, we explore how these platforms elevate efficiency, security, and collaboration for sellers.
🔎 Additional reading: Discover more about due diligence virtual data rooms in our dedicated article.
Centralized document management
Historically, corporate document checklists, a cornerstone of M&A transactions, were managed through static Excel files shared via email, leading to version conflicts and delayed updates.
VDRs resolve this by integrating checklists directly into the platform. Administrators can upload existing Excel checklists without format conversion, preserving familiarity while enabling real-time edits.
This centralization ensures all stakeholders access a single source of truth, eliminating redundant uploads or external file sharing. For example, sellers can dynamically update financial records or legal disclosures, with changes instantly visible to authorized buyers.
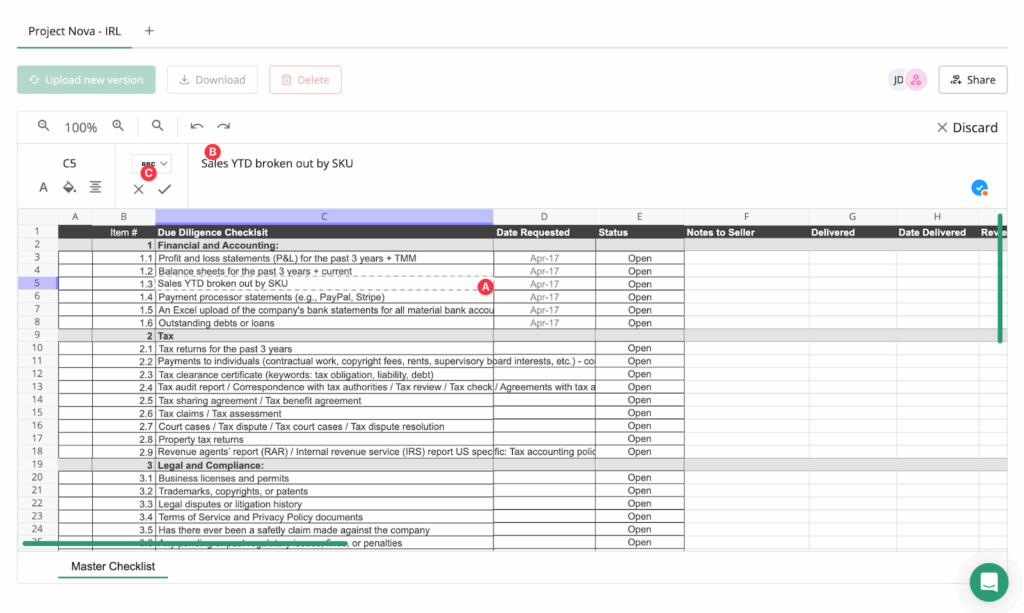
Image: A virtual data room (VDR) dashboard displays an integrated checklist tool, enabling real-time document tracking and secure collaboration.
Enhanced version control and real-time collaboration
Version control is a critical pain point in sell-side diligence, where outdated documents can derail negotiations. VDRs address this by locking parallel editing: only one user can modify a checklist or document at a time, preventing conflicting changes.
Participants with Edit permissions can adjust cell values, formatting, or hyperlinks directly within the VDR interface, with updates saved automatically upon confirmation. This real-time collaboration reduces bottlenecks, as buyers no longer wait for email attachments or manually reconcile changes.

Image: A virtual data room (VDR) interface showcases granular checklist editing permissions.
Granular permissions and security protocols
Security remains paramount in sell-side transactions, where sensitive data exposure risks reputational or financial harm. VDRs enable administrators to assign granular document permissions at the group level, ensuring buyers access only relevant documents.
For instance, financial advisors might have Manage access to business valuation models, while legal teams view redacted contracts.
Advanced security features like IRM (Information Rights Management) add encryption to downloaded files, restricting unauthorized copying or screen captures. Watermarks and audit trails further deter leaks, while time-bound access ensures documents expire post-transaction.

Image: A virtual data room (VDR) permissions menu with IRM (Encrypted) settings for encrypted downloads.
Streamlined workflow and audit capabilities
VDRs automate tedious administrative tasks, particularly tracking document access or managing audit records. Every action, whether editing a cell, sharing a file, or adjusting permissions, is logged in a scheduled audit trail, providing transparency for compliance reviews.
Sellers can also automate buyer notifications: when a checklist is shared, recipients receive an email with access instructions and custom messages (e.g., deadlines). This reduces follow-up emails and ensures stakeholders stay aligned.
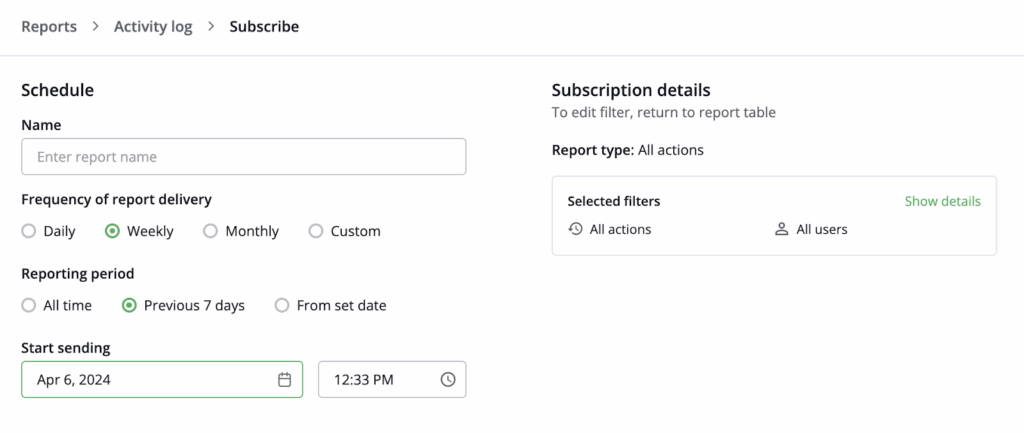
Image: A virtual data room (VDR) interface displays a scheduled activity log menu.
Controlled buyer-seller communication
Virtual data rooms (VDRs) enhance buyer-seller interaction by centralizing Q&A workflows, enabling structured, auditable communication. Administrators assign roles (e.g., Question Submitters, Answer Coordinators) and categorize inquiries (legal, financial) to route queries to experts automatically.
This ensures timely, accurate responses while maintaining version control and permissions. Auto-assign features reduce bottlenecks, while audit trails track every interaction, fostering transparency in the due diligence workflow.
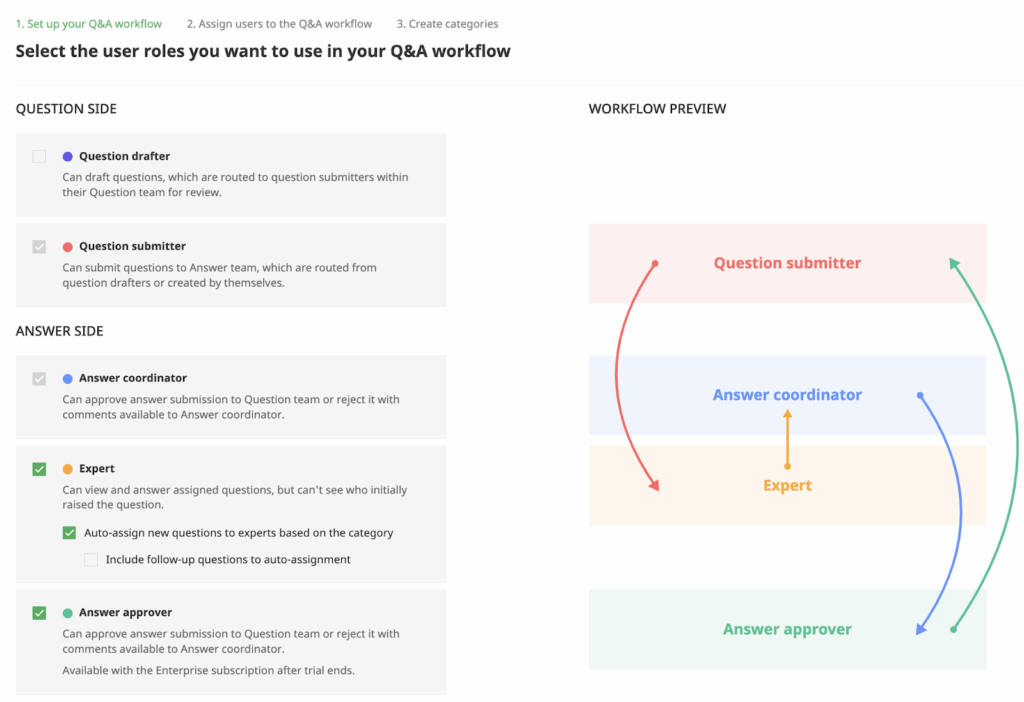
Image: A digital dashboard illustrates a Q&A workflow within a virtual data room (VDR).
Key takeaways
- Proactive due diligence enhances risk management, accelerating deals and boosting valuations.
- Cross-functional teams (legal, financial, operational) ensure comprehensive preparation.
- A structured checklist improves merger readiness, anticipating buyer needs and reducing delays.
- A data room for M&A secures documents while enabling real-time collaboration.
- Transparent narratives and resolved red flags build buyer trust and competitive tension.
- Early preparation aligns stakeholders, prevents surprises, and strengthens negotiation leverage.

