Although the global M&A activity is 44% down compared to 2022 (as of May 2023), buyers still need to close deals and grow their businesses. One of the pillars of a successful deal is proper due diligence.
This deep-dive guide defines due diligence, explains six stages of the due diligence process, discusses four common challenges, and offers four best practices for a successful investigation. Keep reading to discover the approaches, methods, and tools companies use while conducting due diligence.
Understanding due diligence
Due diligence (DD) is a comprehensive investigation that discovers and analyzes information about a matter under discussion. As a term, due diligence appeared in 1598 and meant “The care that a reasonable person exercises to avoid harm to other persons or their property.”
Later, this term migrated to the business context. Due diligence became a common business practice when the US government passed the Securities Act of 1933. The law required brokers to disclose accurate and relevant information about securities. It also enabled investors to conduct meaningful investigations before buying securities.
These days, due diligence refers to the systematic investigation, assessment, and analysis of a company before a business transaction.
Due diligence areas
Quality due diligence focuses on all aspects of the target business. Dealmakers define several types of due diligence based on business areas under investigation:
| Due diligence types | Due diligence process checklist example |
| Financial |
Company’s financial statements |
|
Financial records |
|
|
Cash flow statements |
|
|
Investment decisions |
|
|
Assets and liabilities |
|
|
Historical financial performance |
|
|
Debt-to-equity ratio |
|
|
Off-balance sheet items |
|
| Commercial |
Market info |
|
Competitive landscape |
|
|
Business plan |
|
|
Growth opportunities |
|
|
Customer base and brand perception |
|
|
Historical sales performance |
|
| Human resources |
Management structure |
|
HR policies |
|
|
Compensation policies |
|
|
Employee turnover |
|
|
Workplace culture |
|
| Technology |
IT systems |
|
Infrastructure |
|
|
Governance policies |
|
|
Applications |
|
|
Technology roadmaps |
|
|
Cybersecurity policies |
|
| Operational |
Company’s supply chain |
|
Health and safety practices |
|
|
Operation technology systems |
|
|
Facilities |
|
|
Workforce productivity |
|
|
Quality controls |
|
| Legal |
Corporate structure |
|
Contracts and agreements, like purchase agreement |
|
|
Intellectual property rights |
|
|
Licenses |
|
|
Legal issues |
|
|
Active and pending litigation |
|
|
Legal and regulatory requirements |
|
| Tax |
Tax structure |
|
Tax records |
|
|
Employee tax obligations |
|
|
Tax compliance |
|
|
Tax implications |
The purpose of due diligence
Due diligence is performed when Company A buys, joins forces, or enters into an agreement with Company B. The acquisition due diligence process interconnects with the sales due diligence, so it’s a two-way business.
Due diligence on the M&A timeline:
| 1. Preliminary review | 2. Letter of intent | 3. Due diligence phase | 4. Deal closing | 5. Post-merger integration |
Companies pursue the following purposes while performing due diligence:
- Approach deals strategically. Buying companies build performance projections, identify potential synergies, conduct shareholder value analysis, and prepare for post-merger integration. Due diligence extracts measurable parameters, allowing buyers to understand whether transactions add strategic value.
- Determine deal prices. A buying company evaluates the target’s assets, liabilities, operations, intellectual property, customers, and other aspects to estimate the deal price. In turn, the seller request intends to check the buyer’s financial stability and reputation.
- Identify and address risks. Due diligence is a tool for comprehensive risk assessment during the transaction. Companies reveal and timely address pre-close tax issues, intellectual property litigation, data breaches, and other common M&A risks.
- Streamline transactions. Sellers conduct due diligence to prepare records for buy-side investigation. Structured documentation clarifies the process, shortens the transaction time, and reduces due diligence costs.
Key 6 stages of the due diligence process in mergers and acquisitions
Due diligence process steps involve contract review, governance establishment, planning, investigation, analysis, and negotiation.
| 1. Contract review | Deal parties clear out antitrust concerns and negotiate on sale contracts before signing a letter of intent. If there are several bidding parties in a deal, sellers may conduct due diligence to choose the best acquirer. |
| 2. Governance | After signing the letter of intent, dealmakers establish a DD office to supervise the process of due diligence. |
| 3. Planning | DD office outlines the due diligence terms and assigns DD teams. |
| 4.Investigation | DD teams investigate the target’s business areas. |
| 5. Analysis | DD teams compile, analyze, validate, and report due diligence findings. |
| 6. Negotiation | Based on due diligence findings, deal parties renegotiate the transaction price. |
Now, let’s see the peculiarities of each stage in more detail.
1. Contract review
Before dividing into due diligence investigations or even starting diligence planning, companies conduct preliminary contractual analysis. It is necessary to clear out antitrust law implications and understand whether the transaction is viable in the first place.
Thus, McKinsey’s research on 346 large M&A deals has found that 14% of transactions are canceled due to antitrust regulations. As a result, the upcoming transaction may need the Bureau of Competition’s approval.
Companies may also discuss licensing matters, employment contracts, and other matters, especially those relating to the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA). Afterward, businesses outline these considerations in the letter of intent.
2. Governance
Due diligence planning should start with the due diligence program management office. It consists of top managers and senior executives who oversee the due diligence phases from start to finish.
Many companies take a two-way approach to due diligence governance, assigning buy-side and sell-side executives to the DD management office. Businesses should create this governing body as early as possible.
3. Planning
The DD office should outline the following aspects of due diligence planning:
- Scope. Outline due diligence areas, determine specific documents under research, and draft due diligence checklists.
- Methodology. Develop document review and financial projection standards, establish assessment criteria for business functions and financial health, and define risk detection methods.
- Timeline. Estimate due diligence timelines and outline milestones based on the deal’s complexity.
- Execution. Assign due diligence teams with diverse expertise relevant to business functions under investigation. Involve financial, legal, HR, IT, and other professionals, including external advisors.
4. Investigation
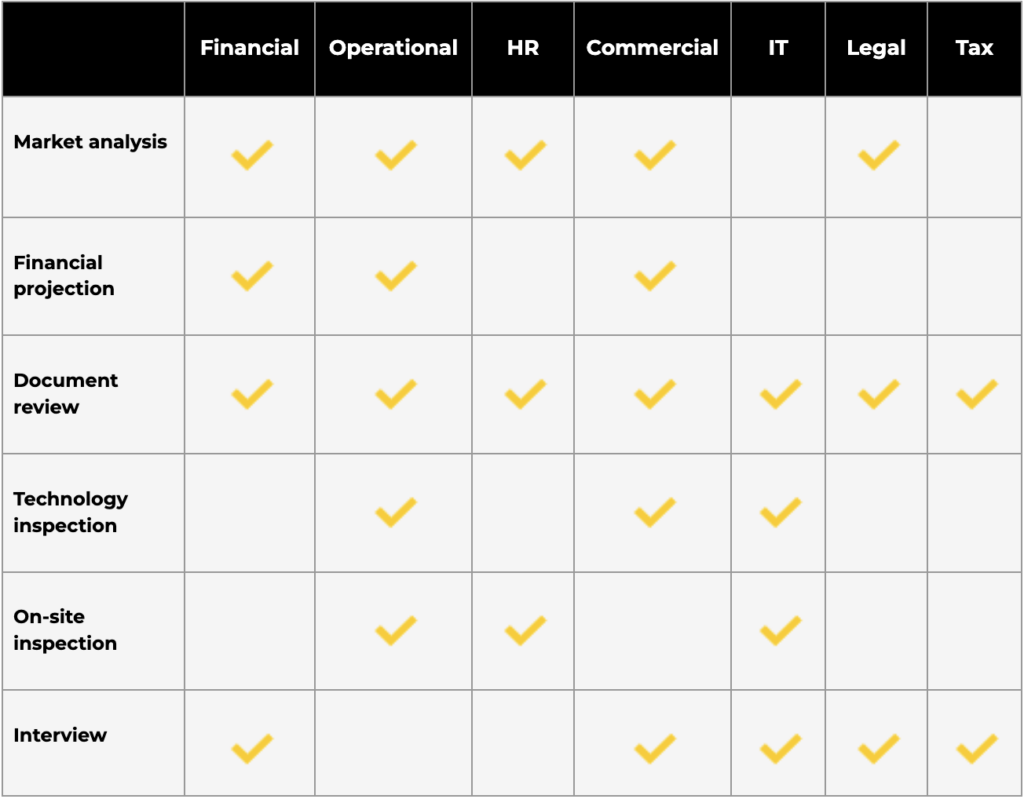
Once the due diligence planning gets finished, the actual diligence begins. During the investigation, deal parties use the following methods:
- Market analysis. The buyer gathers data on the target’s competitive landscape, growth opportunities, marketing strategies, customer relations, etc.
- Financial projection. The acquiring company builds forward-looking estimates, including revenue, profit margin, sales, and expenses projections. DD teams prepare presentations, charts, and graphs for financial analysis.
- Documentation review. The acquiring party requests and reviews the target’s documentation, including but not limited to agreements, licenses, vendor contracts, articles of incorporation, financial statements, and policy statements.
- Technology inspection. The buyer inspects the target’s IT systems and components, including software, hardware, and infrastructure.
- On-site inspection. Buyer’s inspection teams visit the target’s facilities to review physical assets, business operations, environmental and safety practices, etc.
- Interview. The buyer interviews the target’s key personnel, customers, vendors, subcontractors, and business partners for various assessments.
Businesses use these methods for different types of due diligence:
5. Analysis
Here is how to do a due diligence findings analysis works in six steps:
- Data compilation. DD teams categorize and compile findings for further investigation and analysis.
- Cross-reference analysis. Different deal teams cross-reference their data sets, detect interdependencies, and check raw data for inaccuracies.
- Data analysis. The core work begins, including financial reviews, legal audits, and growth projections.
- Data validation. DD teams check research findings and materials for accuracy, tracking back to original data sets and validating results with experts from other DD departments.
- Reporting. Diligence professionals provide due diligence report findings to the DD office.
- Troubleshooting. Acquisition and selling teams collaborate on arising issues.
6. Negotiation
The buy-side proceeds to re-negotiations after validating due diligence findings and making key pricing decisions. The deal parties sign up the definitive purchase agreement (DPA). Afterward, due diligence teams begin researching post-merger integration opportunities, detect synergies, and inspect potential issues.
4 common challenges in the M&A due diligence process
60% of executives say deals fail due to poor due diligence. Let us dive deep into the common challenges of the due diligence process that could lead to that.
1. Communication silos
Due diligence teams often investigate multiple business areas at a time. This approach speeds up the due diligence process in M&A. However, when multiple due diligence teams operate independently, communication silos may occur. Due diligence teams risk not cooperating enough to see the whole picture. Due to poor communication, DD professionals may miss critical interdependencies between findings.
2. Culture clashes
According to Inc, cultural discrepancy is the number one reason M&A deals fail. Based on our experience, cultural issues heavily impact due diligence and hinder decision-making.
Worker relationships, the ability to change, leadership style, and decision-making approach may differ greatly for the buyer and seller. Misunderstandings, inability to adapt, time orientation discrepancies, and reluctant collaboration slow down the due diligence process and reduce its quality.
3. Low data quality
“The concept of ‘garbage in, garbage out’ is particularly relevant in the high-pressure, high-stakes world of M&A.” — Steve Xing, Partner, Business Modeling & Analytics at Deloitte LLP.
Steve Xing, Partner, Business Modeling & Analytics at Deloitte LLP, emphasizes the importance of quality data during due diligence.
Businesses often get frustrated due to low-quality due diligence data. It affects future performance projections and value estimations, hindering the business relationship between deal parties when inherently wrong predictions don’t realize.
Steve suggests that part of the problem lies in poor quality control procedures. Dealmakers often work with disorganized, barely traceable data sets.
Limited data access also plays a role. Unlike publicly traded companies, private companies may not publicly disclose key documents for an informed decision. This is especially true with foreign private investors unless they cooperate with related venture capital or private equity firms.
4. Failure to capture intangible value
Doug Laney, the Data & Analytics Strategy Innovation Fellow at West Monroe, emphasizes that buyers often overlook the value of business data. The contribution of business data to the total corporate value rose from 20% in the 2000s to 80% today.
Customer data, brand equity, intellectual property, business intelligence capabilities, proprietary software, and web presence carry substantial value and may significantly improve transformational synergies.
However, inadequate due diligence may fail to capture this potential. According to McKinsey, poor due diligence may underestimate or miss as much as 50% of the transformative deal value.
Best practices for effective due diligence process in M&A
The best due diligence practices include:
- Cultural due diligence
- Cybersecurity due diligence
- Right technology
- Due diligence checklists
Le’ts review what each of these practices is all about.
Cultural due diligence
Culture clashes are the reason for 30% of failed post-merger integrations. However, according to Bain & Company, 80% of integrations address cultural discrepancies. Still, 75% of mergers experience delays, productivity drops, and misunderstandings.
Bain & Company suggests conducting cultural due diligence and addressing related issues before the deal closing. The best companies dedicate DD teams to culture investigation and relieve collaboration issues early in the M&A lifecycle.
Cybersecurity due diligence
While business data comprise up to 80% of the deal value, it also carries unprecedented risks. According to PWC, 80% of dealmakers uncovered data security issues in their acquisition targets. Additionally, 63% of CEOs consider cyber threats the number one threat to business growth.
Based on our observations, we can conclude that dealmakers still don’t pay enough attention to cyber due diligence in M&A. Meanwhile, cybersecurity due diligence adds the following benefits:
- Reveals security threats. Thorough due diligence identifies system vulnerabilities, past data breaches, and human-related issues. Security inspection also uncovers unexpected cyber threat sources, like current and former employees producing 56% of security threats.
- Ensures customer confidence. About 85% of consumers won’t do business with companies if they doubt their security policies and practices. Conducting cybersecurity due diligence and being open about its results drastically improves brand perception and promotes consumer confidence.
- Optimizes deal costs. Cybersecurity due diligence reveals security-related costs and estimates potential data breach costs. According to Accenture, cyber due diligence can reveal up to $8 million in remediation costs.
Right technology
McKinsey Global Institute found that companies could generate $9.5 – $15.4 trillion in business value with M&A data analytics solutions. McKinsey’s study reveals that data analytics improves all aspects of M&A, including due diligence.
Businesses use data automation software, IT technology, and virtual data rooms (VDRs) for the enhanced due diligence process. VDRs combine data analytics, workspace management, and dedicated M&A solutions.
Virtual data rooms are secure online workspaces where companies manage the full M&A lifecycle, from preliminary research to post-merger integration. It’s crucial to select the data room with tools and features that suit your business case the most. The data room for due diligence helps in the following ways:
- Improves due diligence governance. Geographically dispersed deal parties can collaborate in a central digital workspace. You can share due diligence checklists, review and collaborate on documents, arrange meetings, and sign agreements.
- Eliminates communication silos. Deal parties have real-time access to due diligence materials and can contact each other anytime.
- Promotes top-notch data security. A virtual data room is secure by design, enabling digital rights management tools for utmost data protection. You can use granular access permissions, file encryption, built-in file redaction, version control, watermarks, screen capture blocking, and other tools.
- Enables due diligence analytics. DD teams can easily collect, categorize, and analyze data due to automatic file indexing, interactive file structure, file labeling, advanced text search, and full audit trail. VDRs generate drill-down activity reports to promote better data control.
- Improves cybersecurity due diligence. Accenture has found that 60% of companies still use cumbersome spreadsheets, emails, and disconnected workspaces for cybersecurity due diligence. The data room due diligence process is a much safer, more efficient, and faster alternative to time-consuming legacy approaches.
Check the best data rooms for due diligence
Ideals

- Access controls
- Built-in viewer
- Full-text search
- Auto-indexing
- Customizable branding
- Advanced Q&A
- In-app live chat support 24/7
- 30-second chat response time
Dealroom

- Access controls
- Built-in viewer
- Full-text search
- Auto-indexing
- Customizable branding
- Advanced Q&A
- In-app live chat support 24/7
- 30-second chat response time
Citrix

- Access controls
- Built-in viewer
- Full-text search
- Auto-indexing
- Customizable branding
- Advanced Q&A
- In-app live chat support 24/7
- 30-second chat response time
Box

- Access controls
- Built-in viewer
- Full-text search
- Auto-indexing
- Customizable branding
- Advanced Q&A
- In-app live chat support 24/7
- 30-second chat response time
Intralinks

- Access controls
- Built-in viewer
- Full-text search
- Auto-indexing
- Customizable branding
- Advanced Q&A
- In-app live chat support 24/7
- 30-second chat response time
Due diligence checklist
Acquisition teams often don’t know what questions to ask during due diligence, which may slow down or paralyze the whole process.
Chris Wooley, Partner, Transaction Services at Deloitte LLP, says clarity around the due diligence objective should always come first. When there is clarity, DD teams can harness the full potential of data analytics software and collaborative workspaces.
Based on our expertise, due diligence checklists clarify and streamline both sell-side and buy-side due diligence. Checklists carry a lot of benefits. They:
- Structure due diligence requests. Checklists help the acquisition party outline the required diligence materials for the sales party. They help sell-side and buy-side teams align their efforts and ensure relevant materials receive the necessary attention.
- Simplify progress tracking. Due diligence checklists allow dealmakers to follow a step-by-step procedure, track task progress, and increase accountability. Checklists reduce the risks of overlooking critical details.
- Speed up the document review process. Checklists foster collaboration. They make it easy for DD teams to cross-reference due diligence materials and track issues.
| Learn what you need to include in your data room due diligence checklist. Check the documents required under legal, financial, operational, tax, HR, and other due diligence types. |
Key takeaways
- Due diligence is a comprehensive evaluation of the target company conducted by an acquiring party during the business transaction.
- Due diligence types include financial, legal, tax, operational, technology, human resources, and commercial.
- The purpose of due diligence is to approach deals strategically, identify transaction risks, evaluate deals accurately, and streamline business transactions.
- The process of due diligence in M&A includes initial contract review, DD governance establishment and planning, the due diligence process, findings analysis, and negotiation.
- Communication silos, culture clashes, low data quality, and failure to capture intangible value are the common due diligence challenges.
- Conducting cultural and cybersecurity due diligence, using data analytics tools, data rooms, and due diligence checklists are the best business investigation practices.
- Businesses should emphasize features and functionalities while selecting data analytics tools and data rooms for due diligence.

